Product Details
Buy 99% Pure Threonine 80-68-2 of High Quality with Safe Transportation
- Molecular Formula:C4H9NO3
- Molecular Weight:119.12
- Appearance/Colour:white crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:3.77E-06mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:244 °C
- Refractive Index:1.507
- Boiling Point:345.8 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:2.09(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:162.9 °C
- PSA:83.55000
- Density:1.307 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.52060
DL-Threonine(Cas 80-68-2) Usage
|
Description |
Threonine (abbreviated as Thr or T) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(OH)CH3. Its codons are ACU, ACA, ACC, and ACG. This essential amino acid is classified as polar. Together with serine, threonine is one of two proteinogenic amino acids bearing an alcohol group (tyrosine is not an alcohol but a phenol, since its hydroxyl group is bonded directly to an aromatic ring, giving it different acid/base and oxidative properties). It is also one of two common amino acids that bear a chiral side chain, along with isoleucine.The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttr anslational modifications. The hydroxy side-chain can undergo Olinked glycosylation. In addition, threonine residues undergo phospho rylation through the action of a threonine kinase. In its phosphorylated form, it can be referred to as phospho threonine. |
|
Uses |
DL-Threonine is as an additive to animal feed. They are also used to chelate metal cations in order to improve the absorption of minerals from supplements, which may be required to improve the health or production of animals. This chelating ability is also used in fertilizers for agriculture.DL-Threonine is an essential, non-protein amino acid naturally occurring in the human body and it is involved in many biological processes. DL-threonine takes part in the conversion of glycogen into the glucose pathway, supports muscle tissue maintenance and growth, and plays a key role in regulating levels of other amino acids.L-threonine? is essential amino acids with the physiological effect of DL-threonine being half of that of the L-threonine. Upon its lack, people is easily susceptible to loss of appetite and fatty liver embolism. Threonine can not be de novo synthesized inside the higher animals body and must be supplied externally. The cereal protein, in addition to should being provided of L-lysine, should also be supplied with L-threonine. This is due to that although there is a high content of L-threonine, but the combination of threonine and peptide in the protein is difficult to be hydrolyzed and is not easily digested and absorbed. As a nutritional supplement, in order to play the best use of fruit, it can be co-used with glycine in the rice, co-used with glycine and valine in wheat flour, and co-used with glycine and methionine in the barley, oats as well as co-used with glycine and tryptophan in corn. Co-heating with hot grapes can easily produce empyreumatique and chocolate flavor with aromatherapy role. It can also be used for separation to obtain L-threonine and further for the preparation of amino acid infusion and integrated amino acid preparations. |
InChI:InChI=1/C4H9NO3/c1-2(6)3(5)4(7)8/h2-3,6H,5H2,1H3,(H,7,8)
80-68-2 Relevant articles
A α - amino acid compound synthesis and purification method
-
Paragraph 0069; 0070, (2018/05/16)
The invention relates to a synthesis and...
Preparation and purification method of amino acid compound
-
Paragraph 0066; 0067, (2018/06/21)
The invention relates to the field of in...
Ohmyungsamycins A and B: Cytotoxic and antimicrobial cyclic peptides produced by Streptomyces sp. from a volcanic island
Um, Soohyun,Choi, Tae Joon,Kim, Heegyu,Kim, Byung Yong,Kim, Seong-Hwan,Lee, Sang Kook,Oh, Ki-Bong,Shin, Jongheon,Oh, Dong-Chan
, p. 12321 - 12329 (2014/01/17)
Ohmyungsamycins A and B (1 and 2), which...
New polypeptides inducing apoptosis and uses thereof
-
, (2009/02/10)
The present invention concerns a polypep...
80-68-2 Process route
-
- 1494680-68-0
ohmyungsamycin A

-
- 72-19-5,80-68-2,144-98-9,632-20-2,2676-21-3,7004-04-8,24830-94-2,28954-12-3,36676-50-3,134357-96-3,7013-32-3,82822-12-6
DL-threonine
-
- 2480-23-1,88930-14-7,2566-32-7
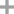
N-methylvaline

-
- 3060-46-6,31321-74-1,2566-33-8
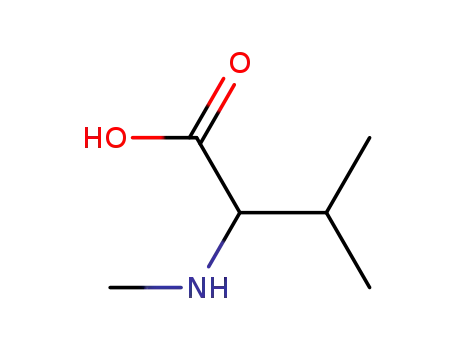
N-methylleucine

-
- 855223-97-1
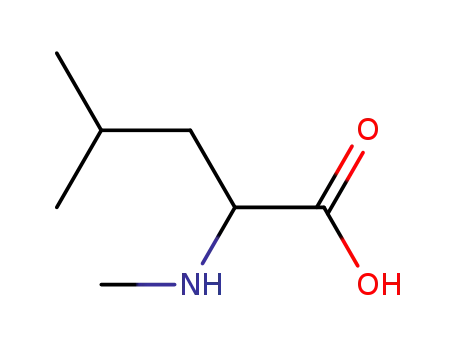
N-methyl-threonine

-
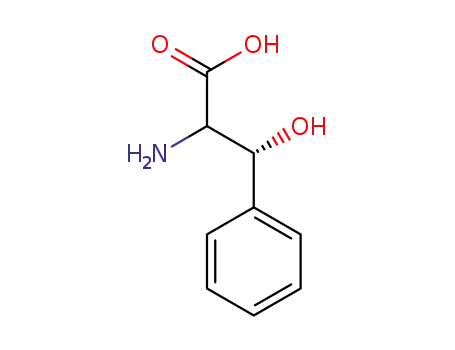
-
β-hydroxyphenylalanine

-
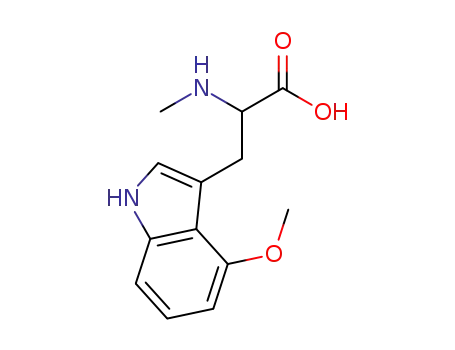
-
N-methyl-4-methoxytryptophan

-
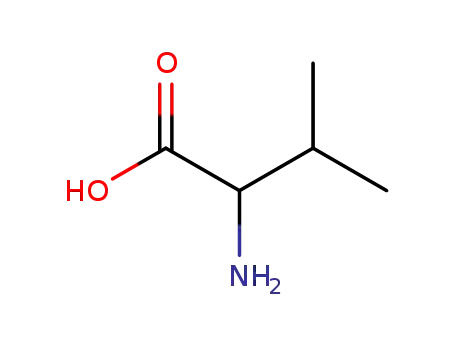
- 516-06-3,25609-85-2,7004-03-7,921-10-8
D,L-valine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; In water; at 115 ℃; for 1.05h; Cooling with ice;
|

-

- 72-19-5,80-68-2,144-98-9,632-20-2,2676-21-3,7004-04-8,24830-94-2,28954-12-3,36676-50-3,134357-96-3,7013-32-3,82822-12-6
DL-threonine

-
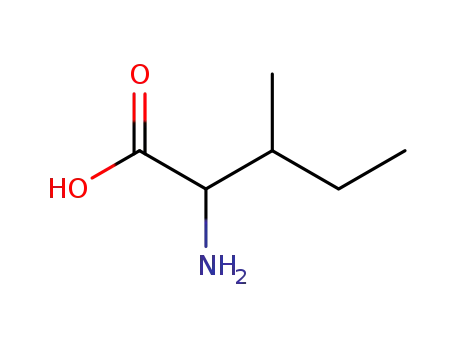
- 319-78-8,443-79-8,1509-34-8,1509-35-9,3107-04-8,7004-09-3,73-32-5,959215-79-3,18875-42-8
isoleucine

-
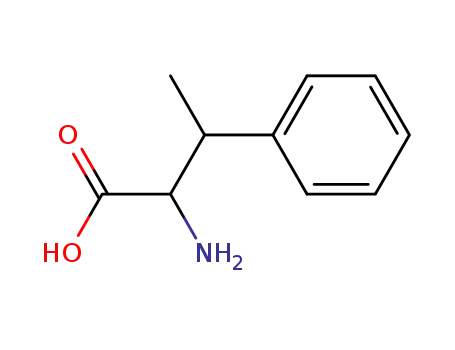
- 2260-12-0,134235-83-9
2-amino-3-methyl-3-phenylpropanoic acid

-
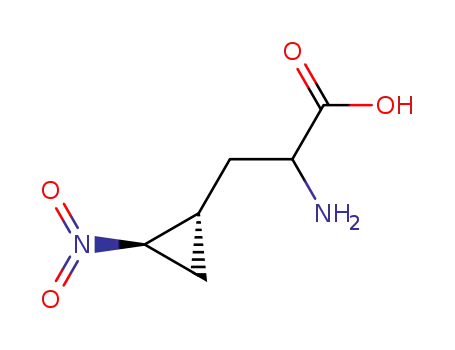
-
3-(2-nitrocyclopropyl)-alanine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; acetic acid; at 110 ℃; for 48h;
|
80-68-2 Upstream products
-
72-19-5
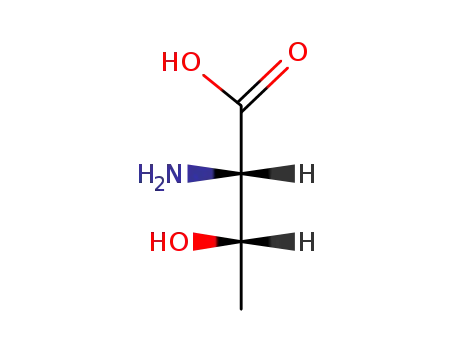
rac-allo-threonine
-
855223-97-1

N-methyl-threonine
-
876367-23-6
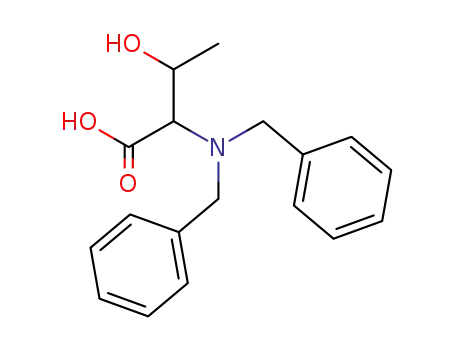
2-Dibenzylamino-3-hydroxy-butyric acid
-
75-07-0
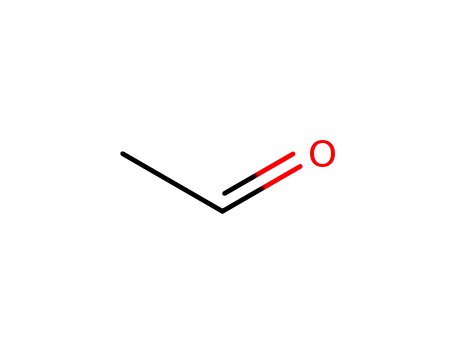
acetaldehyde
80-68-2 Downstream products
-
39994-75-7
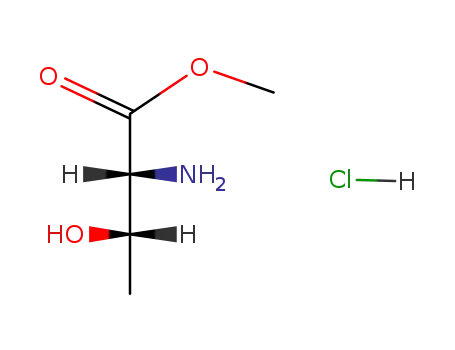
(+/-) threonine methyl ester hydrochloride
-
24809-87-8
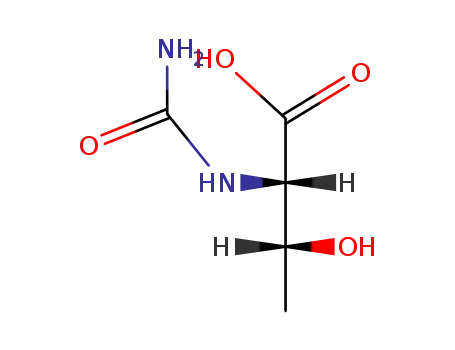
N-carbamoyl-threonine
-
75-07-0

acetaldehyde
-
64-19-7
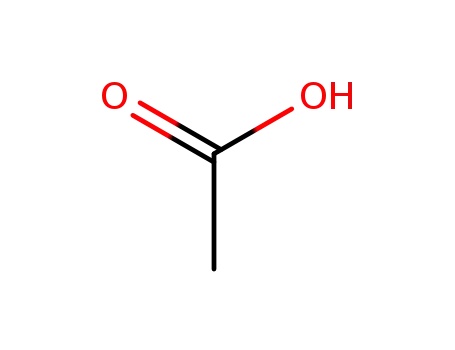
acetic acid
Relevant Products
-
Sodium Citrate
CAS:76-46-0
-
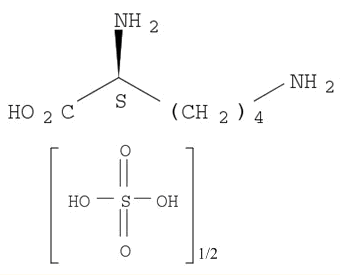
Lysine sulphate
CAS:60343-69-3
-
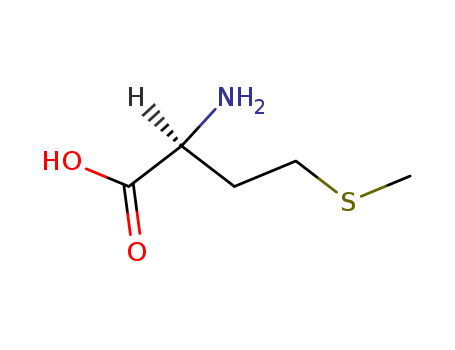
Methionine
CAS:63-68-3