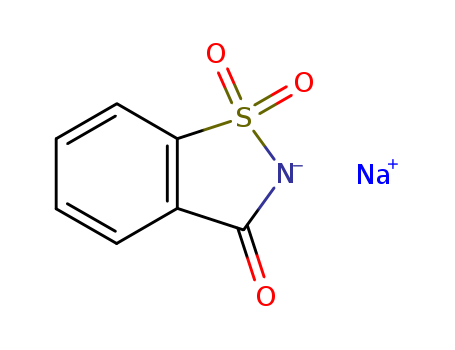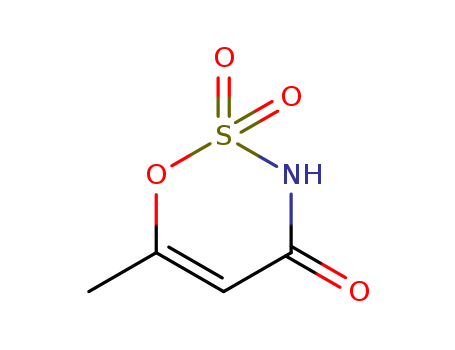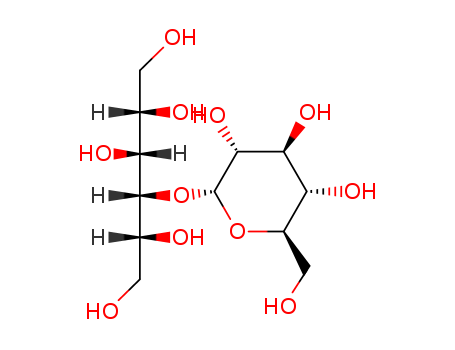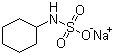
68476-78-8
- Product Name:Sodium cyclamate
- Molecular Formula:C6H12NNaO3S
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:201.22
Product Details
Factory Supply High Purity Sodium cyclamate, Offer 68476-78-8 In Bulk Supply
- Molecular Formula:C6H12NNaO3S
- Molecular Weight:201.22
- Appearance/Colour:White crystal or crystalline powder
- Melting Point:265℃
- PSA:0.00000
- LogP:0.00000
Molasses(Cas 68476-78-8) Usage
|
Description |
Molasses extract is a by-product of the sugar-refining process; the syrup or the “mother water” is separated from the grains of the raw sugar in the process of manufacture. The use of molasses dates back to 1493 when Columbus introduced it to the West Indies. Molasses became an important product in Colonial trade. It was the major sweetener used in America until after World War I because it was less expensive than sugar. The quality of molasses depends on the character and treatment of the cane juices from which it is obtained. Molasses is generally dark brown to bright amber. Blackstrap molasses is the final or exhausted molasses of raw sugar manufacture. Molasses extract is usually sweet; it can also taste burnt. Because of its nature, molasses is expensive to export and is therefore mostly consumed where it is produced. |
|
Uses |
Molasses is the byproduct of the manufacture of sugar from sugar cane in which the syrup is separated from the crystals. the highest grade is edible molasses which is most often found as table syrup. the lowest grade is blackstrap molasses. molasses is a strongly fla- vored, dark colored syrup containing 70–80% solids of which 50–75% is sucrose and invert sugar. it is used in syrups and in the production of caramel. Molasses is used as animal feed (for example in molassed beet pulp), as a food ingredient (where imported cane molasses is mostly used for reasons of taste) and as a raw material in the fermentation industries for the production of yeast, citric acid, vitamins, amino acids and lactic acid as well as for the production of ethanol. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H13NO3S.Na/c8-11(9,10)7-6-4-2-1-3-5-6;/h6-7H,1-5H2,(H,8,9,10);/q;+1/p-1
68476-78-8 Relevant articles
Studies on Synthetic Sweetening Agents. VIII. Cyclohexylamine, a Metabolite of Sodium Cyclamate
S Kojima, H Ichibagase
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1966
The urinary metabolic product of CHS-Na in human, rabbit, and dog was studied. As a metabolite of CHS-Na, cyclohexylamine was found in the urine from human and dog which were received CHS-Na orally. From human urine, the metabolite was isolated as a benzoyl derivative and was quantitatively estimated. In rabbit, however, any metabolite of CHS-Na was not found in our experiment.
Production of Mouse Urinary Bladder Carcinomas by Sodium Cyclamate
GEORGE T. BRYAN AND ERDOGAN ERTÜRK
SCIENCE 13 Feb 1970 Vol 167, Issue 3920 pp. 996-998
Sodium cyclamate was suspended in cholesterol pellets that were surgically implanted in the urinary bladders of mice. In duplicate experiments, incidences of mouse bladder carcinomas observed in animals exposed to these pellets were 78 and 61 percent compared with incidences of 13 and 12 percent in control mice exposed to pellets of pure cholesterol. The exposure of the mouse bladder to sodium cyclamate was very brief, as the time required for 50 percent of the compound to disappear from the pellets was about 1 hour.
Relevant Products
-
Saccharin Sodium
CAS:128-44-9
-
Acesulfame
CAS:33665-90-6
-
maltitol
CAS:585-88-6